

Discrete Manufacturing |
Process Manufacturing |
|---|---|
Discrete manufacturing assembles parts in a prescribed process to produce a distinct item |
Process manufacturing relies on creating formulas or recipes to produce a product |
Discrete manufacturers produce or assemble component or finished products recognized by serial numbers or labeling products |
Process industries make products in bulk quantities, such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and paints |
Products cann be broken down and dispose constituent parts |
Products cannot be broken down into constituent parts |
Uses a bill or materials (BOM) |
Uses formula or recipe |
Discrete manufacturing offers advantages in terms of flexibility, efficiency, quality control, customization, and speed |
Process manufacturing offers many advantages to businesses, including improved efficiency, cost savings, increased scalability, and higher-quality products |
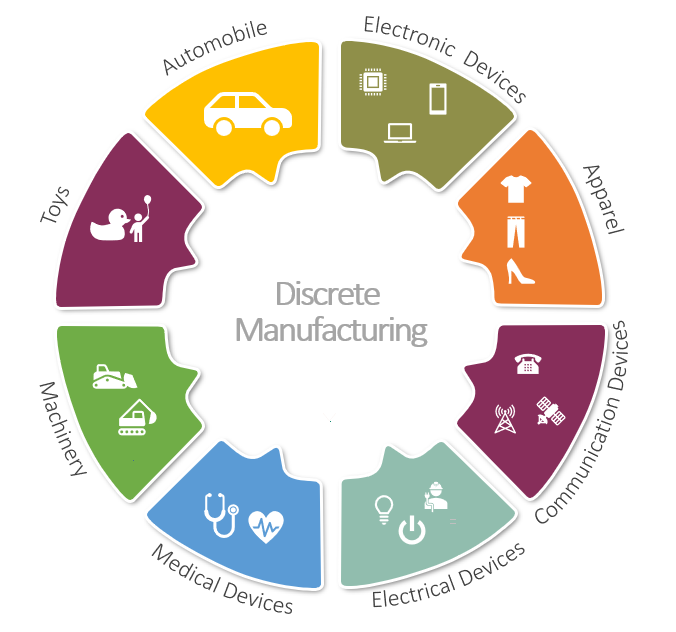
Examples of discrete manufacturing are Automobiles, aeroplanes, Medical devices, furniture, Apparel, toys, Electrical , Communication and electronic devices |
Examples of Process Manufacturing are Food and beverages ,Refined oil, Gasoline, Pharmaceuticals, Personal care products, Cosmetics, Specialty chemicals, Plastics, Metals, Paints, Alcohol |
MES for discrete manufacturing has become indispensable for a high percentage of discrete manufacturers as they contend with new markets, new materials, and new production technologies, as well as a growing complexity in final products and the supply chain that supports them. Companies must sustain or accelerate plant efficiency and productivity, and also realize extreme flexibility in all manufacturing processes.
Key features of MES for discrete manufacturing include:
✓ Integration of regulatory and quality requirements into production operations
✓ Synchronization of production processes across the supply chain
✓ Shop floor visibility to support real-time quality and efficiency efforts
✓ Optimized sequencing of manufacturing operations and WIPs
✓ Instant access to production documentation
✓ Real-time shop floor visibility
✓ Enhanced manufacturing operations and WIPs (work-in-progresses)
✓ Effective management of personnel, including training and certification
✓ Optimized materials and maintenance operations management
✓ Well-planned resource allocation,control and material management
While a small fraction of discrete manufacturing endeavors remain in the realm of manual craftsmanship, the vast majority of discrete manufacturers leverage discrete manufacturing software to maximize both the productivity of their facilities and the quality of their finished products.
Additional benefits:
✓ Greater flexibility and capacity to efficiently manufacture today’s smaller lot sizes
✓ Better management and control of increasingly complex products and supply chains
✓ Efficient regulatory compliance and documentation
✓ Lower production costs
✓ Greater customer satisfaction
✓ The tech-enabled lean manufacturing process
- Technology embedded in modern MES enables mid-market manufacturers to apply lean manufacturing techniques that were formerly unavailable.
✓ Greater investments in cloud
- Increased global customers, enhanced competition, regulatory pressures, and decentralization of operations have led to greater industry investment in cloud-based software.
✓ Improved use of smart devices connected to IoT
- Smart devices have the ability to transfer data between each other. Businesses are finding ways to configure their ERP system to take advantage of these things.
✓ Evaluation of business intelligence for manufacturing
- BI Technology has evolved beyond an IT department responsibility into a real-time data tool to analyze big data. So, decision-makers can use it to improve the business.
✓ Increased focus on maximizing CRM process
- With increased computation, buyers are more informed than ever before. Manufacturers are beginning to invest in improved CRM principles.
✓ Additive manufacturing
- Manufacturers have adopted AR to enhance workflow and productivity. It provides seamless communication and reduces errors.
✓ Agumanted reality
- AM uses only the materials needed for the part, which dramatically reduces waste during production.